Telugu is one of the most prominent Dravidian languages spoken predominantly in the southern regions of India, especially in the states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana. With over 80 million native speakers, it ranks as the third most spoken language in India and holds immense cultural significance. This article delves into the rich history, linguistic features, and cultural contributions of the Telugu language, providing an in-depth understanding of its importance in modern society.
As one of the oldest surviving classical languages in the world, Telugu continues to thrive in literature, cinema, and daily communication. Its rich script, distinct phonetic system, and historical evolution make it a fascinating subject for linguists and culture enthusiasts alike. From ancient inscriptions to contemporary digital content, Telugu has adapted and evolved while retaining its core essence.
Our exploration of Telugu will cover its historical origins, grammatical structure, cultural impact, and modern relevance. Whether you're a language enthusiast, a student of Indian culture, or simply curious about this vibrant tongue, this article aims to provide comprehensive insights into why Telugu remains an integral part of India's linguistic heritage.
Read also:Top Hot Web Series You Should Watch In 2023
Table of Contents
- History and Evolution of Telugu
- Telugu Script and Writing System
- Grammatical Features of Telugu
- Telugu Literature and Literary Contributions
- Telugu Cinema: A Cultural Phenomenon
- Dialects and Regional Variations
- Cultural Significance of Telugu
- Modern Usage and Digital Presence
- Telugu in Education and Academia
- Future Prospects and Challenges
History and Evolution of Telugu
The origins of Telugu can be traced back to the ancient Dravidian languages spoken in southern India. The earliest known inscriptions in Telugu date back to the 6th century CE, found in the inscriptions of the Renati Cholas. Over the centuries, Telugu evolved through three distinct phases: Old Telugu (600-1100 CE), Middle Telugu (1100-1400 CE), and Modern Telugu (1400 CE onwards).
Key Historical Developments
- 6th Century CE: First recorded inscriptions in Telugu
- 11th Century: Emergence of distinct literary works
- 14th Century: Transition to modern Telugu
According to linguists like Dr. C.P. Brown, Telugu has undergone significant changes in its vocabulary, grammar, and phonetics while maintaining its core structure. The influence of Sanskrit and Persian during various periods of history has enriched the language's lexicon.
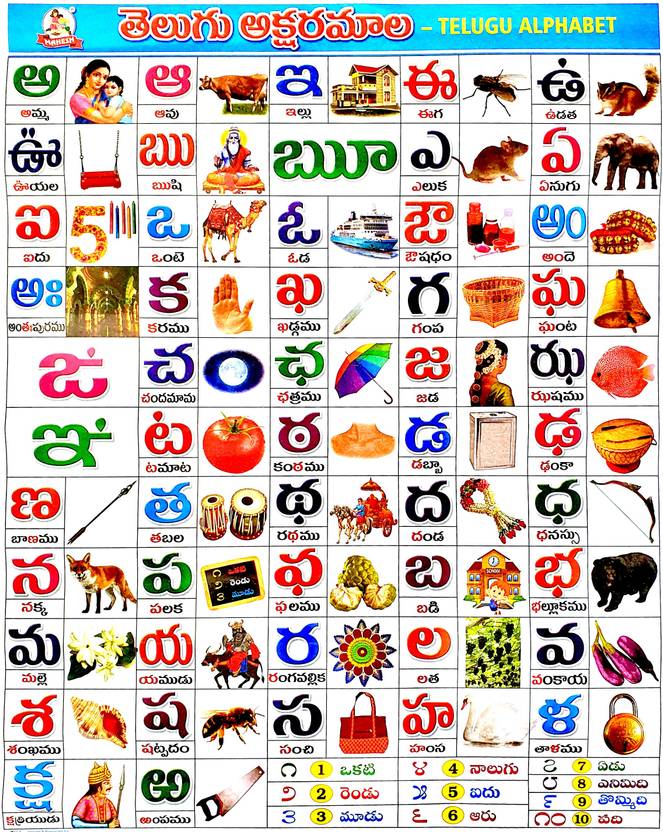
Telugu Script and Writing System
The Telugu script is an abugida, where each character represents a consonant-vowel combination. It consists of 48 primary letters, including 16 vowels and 32 consonants. The script is noted for its rounded shapes and flowing curves, making it visually distinct from other Indian scripts.
Unique Features of Telugu Script
- Distinct vowel diacritics
- Separate symbols for consonant clusters
- Directional writing from left to right
According to UNESCO's Memory of the World Programme, the Telugu script has been preserved in thousands of ancient manuscripts, showcasing its historical significance. The script's evolution over centuries reflects the cultural and linguistic developments of the region.
Grammatical Features of Telugu
Telugu grammar exhibits unique characteristics that distinguish it from other Dravidian languages. It follows a subject-object-verb (SOV) word order and uses postpositions instead of prepositions. The language employs extensive use of suffixes to indicate grammatical relationships.
Key Grammatical Elements
- Agglutinative structure with multiple suffixes
- Eight cases in noun declension
- Distinct verb conjugation for tense, mood, and aspect
Research by linguist Bhadriraju Krishnamurti highlights Telugu's sophisticated system of verb inflection and noun declension. The language's ability to incorporate new vocabulary while maintaining its grammatical integrity has contributed to its longevity.
Read also:Unlocking The Power Of Y Video Open Your Ultimate Guide To The Trending Platform
Telugu Literature and Literary Contributions
Telugu literature boasts a rich tradition spanning over a millennium. The golden age of Telugu literature occurred during the Vijayanagara Empire (14th-17th centuries), producing masterpieces like Nannayya's "Andhra Mahabharatamu" and Tikkana's "Vishnu Puranamu." Modern Telugu literature includes renowned works by Viswanatha Satyanarayana and Sri Sri.
Notable Literary Movements
- Vyasa Kavi Period (11th-13th centuries)
- Prabandha Literature (14th-16th centuries)
- Modernist Movement (20th century)
The Encyclopedia Britannica recognizes Telugu as one of the most prolific literary languages in India, with contributions in poetry, prose, and drama. The language's adaptability to various literary forms has ensured its continued relevance in contemporary literature.
Telugu Cinema: A Cultural Phenomenon
Telugu cinema, often referred to as Tollywood, ranks among the largest film industries in India. Established in 1921 with the release of "Bhakta Prahlada," the industry has produced thousands of films, contributing significantly to Indian cinema's global presence.
Key Contributions of Telugu Cinema
- Innovation in music and dance
- Development of unique narrative styles
- Recognition in international film festivals
According to the Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI), Telugu cinema generates revenue exceeding $1 billion annually. The industry's influence extends beyond entertainment, shaping cultural trends and language usage among younger generations.
Dialects and Regional Variations
Telugu exhibits significant regional variations, with distinct dialects spoken across Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and neighboring states. Major dialects include:
Primary Telugu Dialects
- Rayalaseema dialect
- Coastal Andhra dialect
- Telangana dialect
Research conducted by the Central Institute of Indian Languages (CIIL) documents over 20 distinct dialects of Telugu, each reflecting local cultural influences. Despite these variations, mutual intelligibility remains high, facilitating communication across regions.
Cultural Significance of Telugu
Telugu plays a crucial role in preserving the cultural heritage of southern India. The language serves as a medium for traditional arts, festivals, and rituals. Its influence extends to music, dance, and culinary traditions.
Cultural Contributions of Telugu
- Classical music forms like Kirtana and Keerthanam
- Traditional dance styles including Kuchipudi
- Unique culinary practices and recipes
The Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) acknowledges Telugu's role in promoting cultural exchanges between India and other countries. Its integration into modern media and technology ensures the preservation and promotion of cultural traditions.
Modern Usage and Digital Presence
In the digital age, Telugu has successfully transitioned to modern platforms, with increasing presence in social media, online content, and digital communication. Major tech companies like Google and Microsoft offer comprehensive support for Telugu language users.
Digital Developments in Telugu
- Unicode support for Telugu script
- Development of Telugu input methods
- Growth of online Telugu content
According to a report by the Internet and Mobile Association of India (IAMAI), Telugu ranks among the top languages used on Indian digital platforms. The language's adaptability to modern technology ensures its continued relevance in the digital era.
Telugu in Education and Academia
Telugu serves as a medium of instruction in schools and universities across Andhra Pradesh and Telangana. The language's inclusion in academic curricula promotes literacy and cultural awareness among students.
Academic Contributions
- Establishment of Telugu universities
- Research in Telugu linguistics
- Development of educational materials
Institutions like the Dravidian University and Osmania University play pivotal roles in advancing Telugu studies. Their research and publications contribute significantly to the language's academic recognition and development.
Future Prospects and Challenges
While Telugu continues to thrive, it faces challenges in the digital age, including competition from global languages and changing communication patterns. Efforts are underway to promote the language's usage among younger generations and enhance its digital presence.
Key initiatives include:
- Government support for language preservation
- Development of digital resources
- Encouragement of bilingual education
According to the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE), promoting regional languages like Telugu in educational institutions ensures their continued relevance in modern society. The language's ability to adapt while retaining its cultural essence will determine its future prospects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Telugu stands as a vibrant and resilient language with a rich history and cultural significance. Its evolution over centuries, adaptability to modern technology, and continued relevance in literature, cinema, and education underscore its importance in contemporary society. As we move forward, preserving and promoting Telugu remains crucial for maintaining India's linguistic diversity.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Telugu in the comments section below. For further exploration, consider reading about other Dravidian languages or exploring Telugu literature and cinema. Your engagement helps promote the language's global recognition and appreciation.